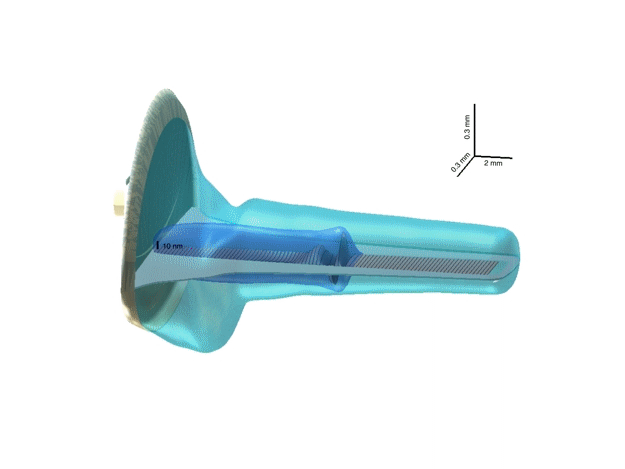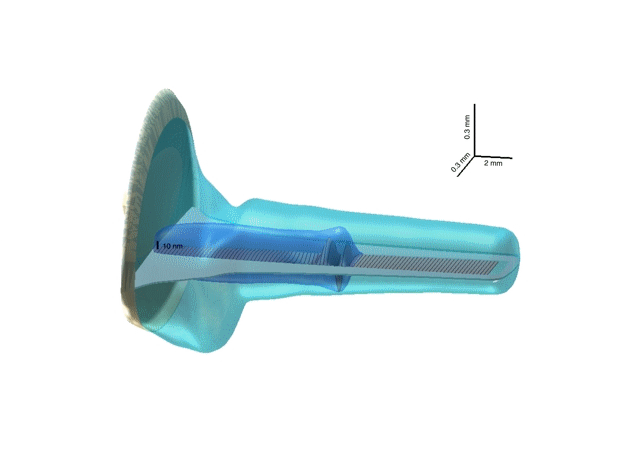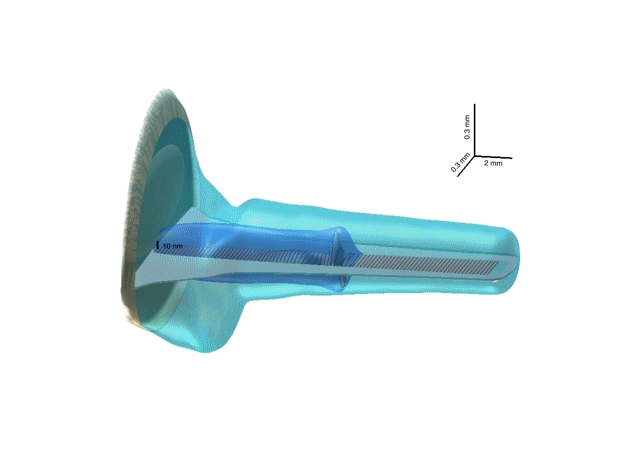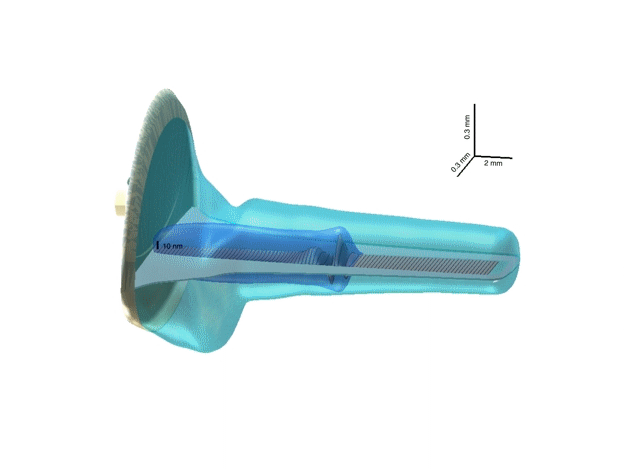
3-D representation of a hydrodynamic cochlea model
Uncoiled
3-D cochlea model illustrates the most relevant cochlea geometric
features: the trumpet-like shape of the cochlea duct and tapering of the
basilar membrane (BM). Note the different scaling of the axes. The BM
could be thought of as an array of damped strings loaded by a local
inertial reaction of the organ of Corti. The primary cause of a BM
vibration pattern is an oscillation of the stapes, which is immediately
(with the speed of sound in water) communicated via the cochlea fluid to
the BM. The mutual motion of the stapes footplate and the BM forms a
pressure difference across the BM (the dark blue TW tail). This
difference is the driving force for local BM oscillators, which then
cause travelling-wave motion of the BM.
© 2005 A. W. Gummer. Animation by Dr. A. Vetesnik.